Paper Doll
Whoopsie! What To Do When Your Week Doesn’t Go As Planned

This isn’t the post I planned to write today.
And last week’s post never got written. In fact, last week did not go as planned at all. It went BOOM!
VERTIGO, BUT WITHOUT JIMMY STEWART
It all started last Sunday evening. I was chatting on the phone with a friend and getting ready to start writing a post for Janet Barclay’s excellent monthly Organizing and Productivity Blog Carnival. Usually I submit a post from the Paper Doll vault, but this time I wanted to write a new post, specifically for the carnival. (We’ll get to that later.)
As my friend and I were talking, I sat on the edge of the bed and then lay down to stretch my back. Immediately, I was overcome with a powerful sense of vertigo — not mere dizziness, or as though the room were spinning, but as though I weighed tons and was going to go barreling through the Earth. While it was not the worst I’ve felt in my entire life, it would rank in the top three.

Publicity Poster from Alfred Hitchcock’s 1958 Vertigo
I’ve had benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) twice before, and both times it was quickly dispatched by a seemingly magical series of movements called the Epley Maneuver. I’ve seen it be such a freaking miracle that I’m a typical explanatory video in this post. (Think of it as organizing for the inner ear!)
Unfortunately, this time, Epley let me down.
The next six hours seemed to pass like jump-takes in a movie. It was 6:35 p.m. and I was on the phone with Paper Mommy. The next thing I knew, it was almost an hour later. And then another hour. My insurance company has Teladoc built-in, and I’d previously registered, so I used the app to reach a physician for a video consult.
As a professional organizer, here’s how I thought it should work: I register for everything in advance (which I had). I click the button and provide my reason for seeking an appointment (which I did). And then I’d be connected with a medical professional.
Nope.
Although I registered for Teladoc when it first became available, I still had to try to type/dictate my medical history, all while lying flat on the floor and spinning. And I had to provide the address and phone number of my pharmacy…which was written on my prescription bottles…in the other room. (Crawling was agonizing. Have you ever seen someone try to do the backstroke on plush carpet? It was not pretty.)
After all that, I got a message saying someone would be with me within ten minutes. Then a message saying that {name redacted} was reading my file. Then a message saying, “Oops, sorry, we’ve canceled your video appointment. If you still need help, please try to schedule another Teladoc appointment.” Seriously?!
As I went through the entire process again, I noted the clock on my phone. I’d have sworn only minutes had passed, but almost another hour had gone by.
I’ll spare you readers the sordid medical details, but by the time I finally spoke to a Teladoc physician, I was instructed to call 911. When I asked why, the response was troubling enough that I only asked if someone could just take me to the ER.
I live upstairs. The prospects of having to go downstairs by myself to let first responders in or having them break down my door were equally unpleasant. Instead, I called my local bestie, Jen, to see if her husband could stay with her kids, and she immediately headed over to take me to the emergency room.
Moms know everything! She arrived with all sorts of Mom Emergency Paraphernalia, including an old-fashioned ice pack.
Although the panic was secondary to the rollicking vertigo and related symptoms, Paper Doll offers a full-service blog atmosphere, so may I also share this advice from Valera Health’s Mastering the Art of Panic Attack Prevention: From Panic to Peace (bolded emphasis is mine):
The keywords here are ice and sweets. If you’re able to, grab a cold washcloth, water bottle or ice cube and rub it on your face. Panic attacks can induce hot flashes so cold stimuli may help you to cool down and calm down, which in turn can shorten panic attacks and make them more bearable. Another way to try this type of sensory grounding is to quickly dunk your head or face under cold water (make sure the water isn’t too freezing first!).
Some people prefer to do the “sour candy trick” instead by sucking on a super sour candy when feeling panicked. The tart taste helps with refocusing and shifting attention away from the symptoms of a panic attack. If you’re prone to panic attacks, we recommend carrying sour candy around whenever you’re out and about so you always have them handy, just in case.
MAKING SENSE IN THE AFTERMATH OF AN EMERGENCY
Once the emergency, itself, is over, you’re left mopping up the mess. Dealing with the aftermath of a natural disaster or a medical situation is usually more problematic than coping with your schedule, but eventually, you’re going to have to turn your eyes to the smoking piles of debris that used to be your carefully planned schedule.
You may not be able to do much right away. I collapsed into bed as soon as I got home from the ER. Though the meds they’d given me had me sleepy while there, my brain was spinning almost as much as the room had been. I had SO MUCH planned for the week prior to Thanksgiving. How would I get back on track?
The following are some of the concepts I put into practice. Whether you have a family emergency or just something that keeps you down for the count, these ideas should be useful until you can see a light at the end of the tunnel.
Assess the Damage
Whether you’ve taken to your bed with the flu or a tree has toppled across your driveway (as happened to so many after this hurricane season), you can’t take action right away. But when you do have a sane, cogent moment to breathe, grab your calendar and your To Do list, and either a pad and pen or a blank Word doc or Evernote note.
Don’t be listless! Take a moment to list everything in your schedule that was disrupted (or will be disrupted).
That first morning was a Monday. Normally I would have completed the weekly Paper Doll post on Sunday night and spent the day doing marketing tasks, sharing my post and those of my organizing colleagues. Again, I hadn’t written the post, which I’d intended to submit to the blog carnival, but even if I had, dragging myself to the computer and lifting my head to the screen was a non-starter. But the world wasn’t going to end because my post hadn’t shown up in someone’s mailbox or social media feed.
Later that day, I had an appointment to get my hair cut, and had blocked time to prepare for guesting on Frank Buck’s Get Organized! podcast on Tuesday.

Tuesday’s schedule included the podcast recording, a first-time physical therapy appointment, a two-hour co-writing session, and two webinars I’d planned to attend.
As the week went on, I had client sessions, prospect consultations, and the variety of life activities (bill-paying, shopping, preparing for this week’s Thanksgiving adventures) that everyone has.
In addition, I had to figure out how (when the world was still spinning, though at a slightly less malevolent pace) to get my prescriptions filled and talk to my own physician regarding some things I suspected I’d need beyond what the ER had advised.
When I floated up into consciousness on Monday, at least I knew what was on my plate.
Prioritize Key Activities
In Use the Rule of 3 to Improve Your Productivity (which I invite you to read and embrace with all your heart and soul and calendar), I reviewed all the ways to manage your schedule and To Do list to keep life from getting in the way. But, as with my week last week, sometimes life is a giant elephant and you have no choice but to let it get in the way.
In that post (and further, near the end of Paper Doll Shares Presidential Wisdom on Productivity) I explained that when you’re overwhelmed, a great way to prioritize what you have to get done (and how and when to do it) is the Eisenhower Decision Matrix.
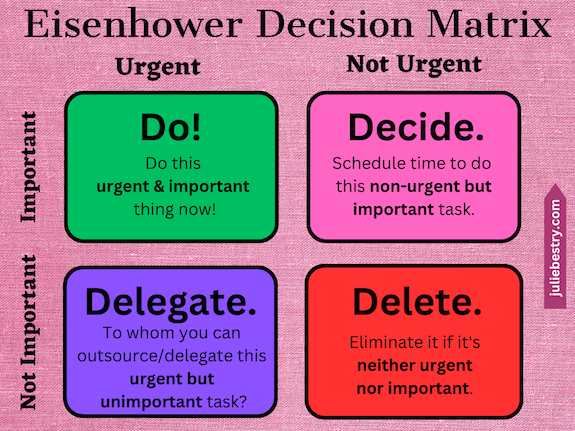
The Eisenhower Matrix gives you the opportunity to graph each task from your brain-dumped list to identify where it falls along a continuum of importance and urgency.
In a typical week of my schedule, what’s important is anything that brings in money, protects from “danger” (whether that’s a late fee or something more problematic), or directly impacts someone else. What’s urgent is anything that is time-specific in the short-term.
Identify What to Do, Decide (and Delay), Delegate, or Delete
Do
As I looked at the tasks, I realized that while my hair cut was not important, it was urgent to cancel so that my stylist would not be inconvenienced by a no-show. The podcast recording on Tuesday would have been both important (to me and to Frank) and urgent. And I had to arrange to get my prescriptions filled, as it turned out that one medication required me to be present at the pharmacy; it couldn’t be filled in absentia.
I sent two texts (to my stylist and to Frank) and arranged to get my prescriptions filled.
Decide
At this point, my wobbly brain decided that I could delay considering anything else until after more sleep. I didn’t know if I’d be able to go to my physical therapy appointment on Tuesday or my client on Wednesday, but I let that be Tuesday Julie’s responsibility. I crawled back in bed.
Delegate
I didn’t really have anything to delegate. I did, however, let my friend and colleague Hazel Thornton know what was going on in case I did not show up to our Tuesday co-writing session or a regularly scheduled Friday night Zoom.
I get it. Delegating is hard. Sometimes, it involves asking for a favor, and most of us are loathe to presume upon others or to seem as though we aren’t operating at 100%.
But delegating — whether it involves asking a friend to take you to the emergency room or trusting your spouse to take care of family responsibilities even if they won’t get done the way you would do them or giving the nod to an employee to handle something you would normally do yourself — is essential.
We can’t do everything. Even if we could, we shouldn’t. Leaning on others — respectfully — strengthens all of our human bonds.

This is my friend Jen, who rescued me. We’re afternoon tea buddies.
Sometime in the mid-1970s, I had a big event happening in third grade. I think I was giving a presentation, or maybe getting an award. Parents were going to be in attendance. But when I woke up that morning, my father told me that Paper Mommy had fallen and cracked her ribs during the night and would not be coming to school. I’m not sure how she managed it in those scant daylight moments before I woke up, but Paper Mommy had already arranged for my sister (eleven years my senior and attending college locally, living in the dorms) to be my plus-one at this event.
If she could have been there, she would have. That’s how Paper Mommy rolls. But she made sure that my eight-year-old self felt loved and valued without schlepping her wounded self to a ridiculous elementary school event. My sister rocked it!
Delete
My plan had originally been to write last week’s post about children’s books on organizing and productivity, and I would have included a link to Paper Doll Interviews Melissa Gratias, Author of Seraphina Does Everything! and talked about both my favorite books in these categories, as well as a few surprises from my childhood bookshelf.
I forgave myself for not writing the post and deleted it from my sense of self-obligation. By the time I left the emergency room, I told myself I could just submit some other post I’d previously written about organizing and productivity books.

For example, I could have submitted Paper Doll Presents 4 Stellar Organizing & Productivity Resources, which referenced Hazel’s What’s a Photo Without the Story? How to Create Your Family Legacy and reviewed her Go With the Flow! The Clutter Flow Chart Workbook.
That post also reviewed Kara Cutruzzula’s Do It Today: An Encouragement Journal, and Ellen Faye‘s Productivity for How You’re Wired: Better Work. Better Life.

I could have submitted Paper Doll Introduces 5 New and Noteworthy Books By Professional Organizers, which reviewed:
- Emotional Labor: Why A Woman’s Work Is Never Done by Dr. Regina F. Lark, Ph.D, CPO® and Judith Kolberg
- Organizing and Big Scary Goals: Working with Discomfort and Doubt to Create Real Life Order by Sara S. Skillen
- Filled Up and Overflowing: What to Do When Life Events, Chronic Disorganization, or Hoarding Go Overboard by Diane Quintana, CPO®, CPO-CD® and Jonda Beattie, M. Ed.
- Mind Body Kitchen: Transform You & Your Kitchen for a Healthier Lifestyle by Stacey Crew
- Perfectly Arranged by Liana George
I could even have have bent the rules and submitted a link to the Book page at Best Results Organizing where I list my favorite organizing and productivity books.
Sigh.
But in the end, I slept through most of the ensuing days and missed the deadline to submit anything at all (likely disappointing nobody but myself). And sometimes, just as we have to tell ourselves that it’s OK to delegate, we have to accept that it’s OK to delete things from our task list.
Although I bowed out of Janet’s The Best Organizing and Productivity Books – Productivity & Organizing Blog Carnival, twelve of my colleagues had great submissions, and I hope you’ll read them. And Sabrina Quairoli wrote a post called Children’s Books About Organizing Their Lives! Although it’s different from what I would have written (or may still eventually write), knowing that topic is out there in the world made it easier to delete this from my list.
Create a Realistic Recovery Plan
Before I was a professional organizer, I was a television program director. Partially because of my Type A personality and partially because the television industry eats people and spits them out, being realistic about what you could get done in a day wasn’t actually realistic.
We were expected to be able to do everything, at any moment. After two days out with the flu, I once almost passed out in the hall and ended up just working on the cold floor where there was nowhere to fall.
That’s wackadoodle.
Nowadays, I teach clients to break down their tasks into manageable steps and schedule them across the upcoming days or weeks to avoid overwhelm.
When your week has been blown to smithereens, you absolutely have to be realistic. Sometimes (OK, often), that means being prepared to change direction more than once. When Tuesday hit, I felt worse (until my doctor called in that additional prescription). I revisited everything on my list, and applied the Eisenhower Decision Matrix again.
I decided to not do anything on Tuesday beyond rescheduling that physical therapy appointment to the end of the week and canceling client sessions. Y’know what? The nice physical therapist was glad I was taking care of myself, and rebooked me without a fee. My sweet Wednesday client was soothingly concerned and called to see if her adult daughter could bring me any groceries when she’d be in my neighborhood.
Everything that I tell my clients — that it’s OK to stop and take care of yourself, and that people will generally understand — was true.
Remember to Communicate
Once you evaluate your priorities and figure out what you have to delay, delegate, or delete, make sure you communicate the essentials to the people who can make your life easier, as long as they know what’s going on. That may be family members, friends, colleagues, or team members.
Set realistic expectations, ask for help where and when you can, and just keep them updated on delays. At some point later, you’ll want to renegotiate deadlines, but until you’re feeling clear-headed and calm, you won’t really know what will fit where on your calendar.
Be Flexible with Replacement Dates
Whatever “whoopsie” of a week you’re trying to recover from, it won’t help to triple-stack the next week. Don’t try to overcompensate and “make up for lost time” — you’ll burn out.
Just as we always discuss when talking about time blocking, set aside blocks of unscheduled time in future weeks to catch up. But don’t fill every block of time. You need buffer time and breathing space.
Reflect On What You Might Do Differently Next Time
We always learn more from our mistakes and kerfuffles than we do from our successes. If your week gets blown up by an unanticipated event, use it as a learning experience.
Block a little time on your schedule for the next week to evaluate how you handled the disruption. Consider what kinds of changes, contingency plans, emergency backup, etc., you might put in place to make next time (and there’s always some kind of “next time”) into a softer landing.
Give Yourself Grace
Julie circa 1999 would have tried to show up for work the next day, and attempting to barrel through every task, even while dizzily wobbling into colleagues and walls and copy machines.
Julie circa 2024 made sure that nobody was left in the dark, didn’t over-apologize, and got about 18 hours of sleep each day for most of a week. And everything turned out fine.
Appreciate Normal Weeks
Organize Your Sleep When the Clocks Change and Beyond

Are you feeling wonky? If you live in North America, you turned your clocks back (or let all your digital ones do it themselves) over the weekend. (If you live in the UK, you did it a week ago. I don’t know what’s up with that, but you may still be feeling wonky.)
Although most of the negative effects of time change happen when we are springing forward to begin Daylight Saving Time, falling back to end it can still leave people struggling to wake up and feeling out of sorts for a few days, leading to some bumps in productivity.
So, if you’re feeling a little rough, don’t worry. Today’s post offers some gentle tips for feeling a little more at ease when the time on the clock and the time inside your head don’t feel friendly toward one another.
HELP YOUR BODY ADJUST TO THE TIME CHANGE
Whether you’re dealing with the time change in the spring or fall, the best way to adjust is always to shift your schedule gradually.
Unless you’re the kind of person who misses all the reminders about the clock change and shows up an hour late (or early) to Sunday brunch, or worse, for work on Monday, you have advanced warning. When the time change is on the horizon, adjust your bedtime and waking time by ten or fifteen minutes each night for several days prior. (Make a note on your calendar to start this at the beginning of March; Daylight Saving Time starts on March 9, 2025! I’m already counting down.)
This kind of incremental approach is supposed to give your body the time to adapt. Of course, we’ve just changed the clocks, so that option is out. Still, consider the following steps for helping your body adapt to the time shift. You’ll find that these steps are generally the same ones for attaining recuperative sleep, overall.
Be the Early Bird and Get Morning Sunlight Exposure
I’ll be the first to admit, I’m terrible at mornings. I’d happily take a flight or attend a Zoom at 3 a.m. before going to sleep, but I’d be hopeless doing the same things at 7 a.m. Early morning sunlight makes me growl. However, my science-y pals swear that natural light will help reset our internal clocks.
The research on circadian rhythms says that cycles of sunlight and nighttime darkness keep our bodies synchronized with our environment and signal our “circadian pacemakers.” This pacemaker is particularly sensitive to light in the morning and the evening, so evening light (such as we have all summer) causes a phase delay, so we don’t get tired until later and then we wake up later. Conversely, when we are exposed to bright sunlight in the morning, it causes a “phase advance,” and we start getting sleepy earlier and awaken earlier.

Sunrise Coffee Photo by Taryn Elliott
So, exposure to sunlight signals your body that it’s time to wake up; just some light permeating through your eyelids will have some kid of wakey-wakey-eggs-and-bacon-y effect. So, actually spending twenty minutes outside in the morning will help you feel less sluggish.
If the temperature allows it, take your breakfast out onto your back patio or balcony; you can enjoy your morning coffee on your front step, but if you amble out in your jammies, at least make sure you’re properly covered up as the school bus goes by.
Improve and Optimize Your Sleep Environment
We hear it all the time: it’s important to set a consistent sleep routine.
If you’ve been living the life of a college student (or a new parent) and are all out of whack (and this has been compounded by the end of Daylight Saving Time), be patient with yourself. Know that your body will need time to adjust to whatever changes you make, but sticking to a regular bedtime and wake-up schedule (sigh, even on weekends) will improve your odds of getting better quality sleep and more of it.
Research shows that your sleep experience will improve if you consistently do the following:
- Keep your bedroom dark. Close your blinds or curtains. If you have old-style horizontal Venetian blinds, you may find they let in too much light. If so, try twisting them “backward” such that the curved portion faces outward. Alternatives are the more modern, wider, vertical blinds or roller shades in darker colors.
Another great option is a blackout curtain, which is designed to eliminate as much natural light as possible. Note that the longer the curtain extends from the bottom of the window toward the floor, the less light will seep out.
How to Collect, Organize, and Preserve Family Memories and History (Part 3) — AI & More

Who are you?
Certainly, you are your tastes and preferences, talents and experience. Nobody else has your abilities, quirks, and ways of delighting the world. Much of that comes from everything that’s happened to you, and everything you’ve decided to do (and to not do) since the days you careened onto this mortal coil.
But your very existence, in some ways, is due to those who came before. You enjoy the privileges or suffer the consequences of hundreds of years of decisions and experiences of your ancestors. War and famine, immigration and partner choice — other people’s lives determined, in large ways and small, your life.
Had your parents or grandparents or great-grandparents not come to the country where you were born, you would have had a completely different set of benefits and struggles, whether that’s bountiful nutrition and career opportunities or financial and educational injustices. We end up where we start as the result of our forebears.
Sometimes that means we’re always fascinated to know more about them, and sometimes it doesn’t occur to us until too late in the game to ask questions at all.

This mid-1950s photo shows Paper Mommy, sandwiched between her Bubbe (grandmother) and her mother, with her aunts flanking them. The first several times I asked about this photo, the only thing my mom shared was that she hated her haircut. Asking questions may take perseverance.
We recently did a deep dive into why we might want to know about our family histories and stories, and what questions can help satisfy our curiosity about things we might not even know to ask. Then, we looked at some of the major options for helping collect, organize, preserve, and share those family legacies. In case you missed those posts, you can pop over and read them here:
How to Collect, Organize, and Preserve Family Memories and History (Part 1) — The Questions
How to Collect, Organize, and Preserve Family Memories and History (Part 2) — The Methods
Today, we’re going a little further afield to see what other options may help you embrace those generational memories.
USE AI TO CREATE YOUR FAMILY LEGACY IN PRINT
Artificial Intelligence gets fancier every day. It also gets scarier.
I like when I ask ChatGPT to give me advice on how to make a blog post subject line more friendly for search engine optimization. I don’t like it when it makes things up out of whole cloth.
For example, in 3 Simple But Powerful Productivity Resources — Right in Your Browser Tab, I talked about Goblin.Tools, a 7-in-1 AI tool to help both neurodivergent and neurotypical users with time management as well as “tone” management. On the other hand, my colleague Hazel Thornton has written about both the good and the bad in AI in posts like The AI Gold Rush.)
In this series on collecting, organizing, and preserving family memories and legacies, I wanted to include these AI solutions as opportunities, not recommendations.
Recording audio or shooting video or turning narrated stories into written chapters is a lot of work. Grandma probably isn’t up for it. You also may not have the time for it.
AI, however, has all the time in the world. Why not give AI the chance to play the legacy-preserving version of The Jetson‘s Rosie the Robot and let it do a little of the scut work for you?
For example, if you narrate a story and the AI adds flourishes, creates chapter titles and sub-headers, and formats what you’ve spoken, you’re not wedded to it. You can always revise it. But you can’t edit a blank page, and getting something down is better than waiting until you can make it perfect.
The following are some AI-assisted options for collecting, organizing, and preserving your family stories.
Otto
Otto is an AI biographer, billing itself as a solution to create “memoirs for mere mortals.” It’s based around a simple voice interface, so you just start talking about whatever you want to share: your personal memories, family stories, life milestones, or recapped adventures.
You or your storyteller will get a prompt to answer some questions for about 10-20 minutes, making this ideal for anyone who may feel cowed by the idea of having spin a long yarn. You’re not doing an HBO stand-up special, just ten minutes of responses to weekly encouragement.
Once you’ve done your part, Otto creates transcripts of your recordings and uses artificial intelligence to develop a biography based on what has been said.
Open the app, hand the phone off to Dad, perhaps with a list of prompts (such as the ones I offered in part 1 of this series) and let Otto do the rest.
Otto creates chapters — the transcription is just the first part; the AI magic comes in almost as quickly as you can dictate. Review the chapters as Otto drafts them to ensure that everything you wanted to capture is there.
Worried AI might goof up and misunderstand something you say? The founder, Ashita Achuthan, noted that AI gave her name a few confused looks. So, Otto allows you to go into the transcripts and manually edit to ensure everything looks as it should.
The resulting biography, from what I can tell (without signing up), is digital; if you want a tangible copy, you’ll need to download the content (and perhaps combine with photos) to achieve a DIY book (such as I described in part 2 of this series).
Start with a free, 15-minute introductory trial of Otto to see how a chapter can be created with just a little chat. After that, a lifetime membership is $199, though Otto is in beta (having just launched this year), so the early bird price right now is only $99. With your lifetime membership, you get a 40-chapter biography, automatic transcripts, and access to new sessions and features.
introducing otto
it’s an app that turns your memories into memoirs
show up everyday for 10-20 min sessions
no prep needed. show up and talk
get chapters as you finish each session751 people using otto over last 6 weeks@_buildspace pic.twitter.com/lKmZtxcCC2
— ashita achuthan (@ashitaa) July 27, 2024
Ottostory
Don’t confuse Otto with Ottostory. (Gee, how could anyone confuse the two?)
Ottostory has a three-step approach for building a biography.
- Speak into the phone and Ottostory captures the experiences. It can be a long narrative, a childhood memory, or a life event.
- Select a tone. Depending on the individuals and the story being told, you may want a different tonal or writing style. You get to pick whether the tone should be “adventurous,” “romantic,” or “true to life.”
- Watch your stories become a book. Once all of the tales have been narrated and AI edits the content, the story becomes a bound hardcover book, shareable with family and friends.
Ottostory has a number of features to achieve the narrative result:
Flexible Interaction
First, Ottostory offers multiple input formats. You can integrate voice, text, and document uploads. Enrich your narrative with photographs.
As mentioned, you can select different tonal styles for the writing. You can also invite family and friends to contribute guest chapters, augmenting beloved memories with multiple perspectives.
Guided Storytelling
The process starts with Ottostory’s library of 200 prompts, developed by cognitive behavior therapists, professional authors, and publishers to “elicit meaningful and heartfelt responses.”
If you’re a writer, you may love the idea of taking all the transcriptions of Great-Grandpa’s circuitous stories and editing them into a comprehensible and comprehensive whole. If you’re not, you won’t.
Otto promises that their cutting-edge AI-powered storytelling technology will “seamlessly weave your memories into a compelling narrative” so you can take those stories, eliminate the repetition and excess, and make it make sense.
Once the individual memories are captured, Ottostory organizes the various tales along a structured timeline of key milestones or life events. Instead of a mish-mash of tales, it yields an orderly biography.
Ottostory also offers up to three hours of one-on-one coaching with professional biography writers to help craft your narrative and conquer any writing obstacles.
Customization
Users can custom-design a high-quality, premium book cover based on templates.
Once it’s all put together, you get both a bound hardcover and a digital copy of your book, enabling you to maintain a legacy copy for future generations and share your story now with loved ones wherever they are.
Timelines to complete an entire book vary, but the FAQ says that on average, an autobiography is completed over nine months. There aren’t any time limits, so your storytellers won’t be rushed and can work at their own pace. However, Ottostory helps users stay focused by providing a personalized schedule with reminders to keep going until the book is done.
Ottostory’s pricing is definitely higher than we’ve seen with the other services. It’s $499, for which you get a 7″ x 10″ hardcover book, including fifty pages for narrative storytelling and thirty pages for vivid pictures.
Memoirist
On the opposite end of the price spectrum is Memoirist, an AI-assisted biography and memoir service.
To get started, decide whose life story will be told, whether that’s you, a family member contributing their own tales, or the family genealogist.
Then, Memoirist offers prompts to entice the storyteller to relay important memories. Unlike the other platforms we’ve looked at, Memoirist then has its Interview Helper follow up on those stories with “gentle, insightful follow-up questions to deepen the narrative.”
Access Memoirist on your phone, tablet, or computer.

The AI takes it from there, turning the recorded “conversations” (between the storyteller and the AI) into a compelling story designed to “capture[s] the essence of your experiences.”
Once the story is massaged into final form, personalize the ensuing tangible book with various design options. You can customize the cover and final layout to reflect your preferences based on the kind of memories relayed.
Finally, users may order bound, high-quality print copies to be shipped and shared with family and friends.
Right now, early adopters can try Memoirist for free (discounted from $10) for an initial five chapters; it also includes use of the Interview Helper’s follow-up questions and a formatted PDF of your story.
If you like Memoirist, you can upgrade to a full version for $29 (discounted 70% from the full price of $99). In addition to the assistance of the Interview Helper, you can have up to thirty chapters (up to 200 pages) in a printed, hardcover biography. You also get “do-overs” of the five initial chapters from the trial experience.
Life Story AI
Life Story AI has three approaches. If you’re with your loved one, you can ask them the Life Story AI prompt questions; they can respond using the phone app and be recorded. (They or you can also type answers on the screen.) If you aren’t present and they’re comfy with technology, “Lisa” (the AI) can prompt them to answer directly. Alternatively, sub yourself in to answer the family history questions. There’s no obligation to answer everything.
Based on answers to the general prompts, Lisa will ask customized questions. The platform gives an example of, “As an only child, what kind of fun did you have?” From there:
- Lisa sends a new question weekly, by email. You or your storyteller can answer as many questions as desired. You can add photos to make the story more robust.
- The system records and transcribes everything, and can correct grammar and spelling.
- Edit or delete text as you like, and even add your own preferred questions or stories.
- Once they (or you) have put in 10-20 hours of material, the Life Story is ready to become a book.
- You can adjust the style from the storyteller’s tone to a more literary one.
- Customize the cover of the book — choose a title and import a cover photo.
- Add up to 40 color or black-and-white photos.
The end result is a 250-page printed, soft-cover book with high-quality paper for $99. Additional books can be ordered at $35/each (plus shipping).
AI Life Story
AI Life Story (see what I mean about similar-sounding names?) is yet another AI-assisted book biographer. Once you sign up for an account, your storyteller gets to chat with AI Life Story’s AI interviewer. The interviewer will pose various biographical and thought-provoking questions about backgrounds, interests, and opinions. The storyteller can respond by typing or voice recording.
Once the “interview” is complete, the AI will write a “compelling” story based on the responses. In turn, you can review and edit the story to your preferences. You also have the option of uploading photos and adding comments or other answers, as well as customizing the end-result by choosing from a variety of templates.
The collaboration yields a digital (not printed) book about your life.
There’s a free trial, after which there are two pricing options: monthly for $29/month (currently discounted for early adopters to $25/monthly) and an annual subscription of $228/year (currently discounted to $159/year.
USE AI TO CREATE YOUR FAMILY LEGACY IN VIDEO
And now for something completely different.
Storyfile
You know William Shatner. Whether your Shatner is Captain Kirk, TJ Hooker, or Denny Crane, as spokesperson for Storyfile, he’s got thoughts on preserving video versions yourself (as if you were a holodeck character on the Enterprise) to interact with future generations.
After setting up an account with Storyfile, you log in and select the questions you want to use as prompts. Storyfile has 1600+ questions, grouped as related topics, crafted to encourage vibrant storytelling. Categories include topics covering family traditions, events like vacations and weddings, “favorites,” holidays, children, etc.
In addition to typical biographical questions and genealogical prompts, there are extensive questions in categories we haven’t seen on other platforms, like military memories, prompts for Holocaust survivors, memories about 9/11, questions about personal and family COVID pandemic experiences, “Pride” tales of coming out and gender identity, and more.
The storyteller records their video responses (on a computer, tablet, or phone).
Now, you can share the interactive StoryFile via social media, email, or text. Visiting loved ones can then interact with the videos and find the answers within the StoryFile.
Think of it as a little bit like artificial intelligence setting up a Zoom call and blending it with time travel, yielding an almost sci-fi-like experience for family members to have face-to-[recorded]face interactions.
It’s called conversational video. StoryFile sees itself as transforming one-way video into interactive two-way conversations. Imagine recording your answers and now (or later), your great-grandkids can ask your StoryFile questions. The StoryFile AI then searches the video database of what you’ve already recorded and yields the best video response, making it (mostly) like a conversation. Again, kind of like the Holodeck.
To see it in action, watch the clip of CBS Sunday Morning from this past Memorial Day, showing how the WWII Museum is using this kind of interactive technology.
StoryFile offers a free trial, with which you get 33 free questions, unlimited conversations, the ability to share to social platforms, and one-minute video answers. (Video recordings are 720p resolution.) From there, StoryFile offers three levels:
- Pay per question — For $1 per question, you can select from any of the 1600+ questions to add to the 33 from the free level. You still get unlimited conversations, the ability to share on social media and 720p video recordings, but at this level the video answers are two minutes in duration and you get the ability to re-record your answers.
- Story Pack — For a one-time $49 fee, you can select 75 unique questions to add to the initial 33 and get everything else available at the pay-per-question level.
- Premium — For a one-time $499 fee, you get access to all 1600+ questions in 70+ curated life topics, unlimited conversations, the ability to share on social platforms and re-record your answers plus you can record five-minute video answers. (I’m sure they created this option for people like Paper Doll, for whom brevity is difficult.) Additionally, the video recording quality is 1080p (high resolution) and you get unlimited storage capacity.
USE AI TO CREATE YOUR FAMILY LEGACY IN A MIX OF MEDIA
Memory Lane
Memory Lane is a fairly new platform that seems to take AI one step beyond what we’ve seen so far.
Users — they call them “Storytellers” just as I’ve been saying throughout this series — respond to personalized prompts from Memory Lane’s AI interviewer, recording their memories. These can be stories, family recipes, private jokes, or advice on how to raise children or interact with the world.
The AI interviewer is designed to invite a conversation, not an interrogation. Trained to be “empathetic, patient, encouraging and kind,” their AI is developed by advisors — psychologists, experts in ethics, and professional biographers — to create an interactive interviewer to draw out the best from each Storyteller. In their words, they seek to prompt, “a nostalgic trip down memory lane – and at every step we’ve built our platform with deep respect for the profoundly personal, meaningful experience that is curating your legacy.”
After the interview, recorded answers are stored “forever” in Memory Lane’s private, secure database.
As each storyteller shares more personal and family stories, the AI automatically generates a professional summary and what Memory Lane calls a life story map as a record for future generations, whom they call “the Listeners.” (Again, this starts to feel like Star Trek again, only instead of “Who Watches the Watchers,” it becomes “Who Listens to the Storytellers?”)
Memory Lane offers a 7-day free-trial, after which there are two pricing options:
- a monthly subscription is $8.99/month with unlimited storytelling, 100% personalized questions, unlimited access for the entire family as “Listeners,” narrative tracking (to eliminate errors and make certain no details fall through the cracks), and one color-printed hardcover biography. (After six months of the monthly subscription, the book is free.)
- a one-time annual subscription for $99 provides a full year of access to Memory Lane, all of the features offered with the monthly subscription, and the hardcover book is free to be printed at any time.
Memory Lane is in beta, so some things may not be ready for prime time. (A few of the links are still wonky.)
OTHER LEGACY-PRESERVING OPTIONS
As I researched traditional and AI legacy-capturing options, I found that, just as with productivity and note-taking apps, or almost anything else you can find on the web, there are numerous options without lacking clarifying information. As always, buyer beware.
Of course, you could always hire a professional biographer to speak with your beloved family members. Consider starting with Biographers International Organization (BIO).
Finally, if you and your family are just getting started with pondering how to capture family history, just start asking questions.
Tales
Recently, an ad for a card deck/game appeared on my feed. (Yes, our AI overlords and their sneaky browser cookies are eavesdropping on my research.)
It’s called Tales, and its Life Story interview kit features 150 conversation starters, segmented into three life stages: early life, mid-life, an later life reflections. The arrangement is designed to yield a smooth conversational flow and spark memories and discussions.
Tales is available directly from the creator’s site, above, or on Amazon for $14.99.
How to Collect, Organize, and Preserve Family Memories and History (Part 2) — The Methods

Last week, in How to Collect, Organize, and Preserve Family Memories and History (Part 1) — The Questions we looked at why you might want to collect family memories and stories.
It’s easy to think that it’s all about “genealogy,” which can seem like a dry topic to those who haven’t delved into wacky and wondrous family stories. But we saw how embracing family history can do more than clarify what’s happening in family photos (or make those strangers in black-and-white come alive and feel more three-dimensional). Family stories can help tether us to a genetic continuum and weave us into a tapestry going back generations and extending broadly across time and locations.
For example, when I started my business, I felt like I was adrift, the first person to really “start” a business. When asked for her profession, Paper Mommy usually puts down “part-time brain surgeon” for fun, and while motherhood is an intellectual and physical triumph, it doesn’t ecacly bring in the Benjamins. My father was an attorney and judge, but in the late 1940s, he joined an already existing practice.
But focusing on those stories I told you last week, I can place myself along a continuum of business owners: my material great-grandfather owned his own bakery (with my great-grandmother, who ran it); my paternal grandfather, who co-owned a tailors’ notions shop; my maternal grandfather, who traded in scrap metal (though decommissioned battleships seem more grandiose than “scrap” would imply).
Last week’s post also detailed a wide variety of questions to help get conversations started about family history and memories. We know that some people (and some generations) find it hard to talk about themselves, so it’s no surprise their children don’t ask questions; they don’t realize there’s anything to ask! Hopefully, the prompts I provided last week will give you a starting point to talk with your family about the rich tapestry of their lives.
But what will you do with these stories once you’ve gathered them, and how will you preserve them for future generations?
HOW TO CAPTURE MEMORIES AND STORIES — THE BASICS
Capturing your loved ones’ stories can be as simple or as robust as you choose, and you don’t necessarily have to invest in apps or platforms in order to create a record of someone’s legacy.
Take notes
Start with the basics. If you just want to make sure you get the details of what happened, you could take notes as your Grandpa tells his stories.
Scribbling notes by hand can be more surreptitious; even though we know that taking notes on our phones or computers is more efficient, and putting them into Evernote or even a Google doc will come easily, typing while they’re talking may seem dismissive to older folks. (Don’t we all feel like our doctors aren’t paying attention to us when they stay buried in their computers, tapping away as we describe our ills?)
There are only slightly more complex technological options that, once they are set up, allow you to interact more freely and naturally.
Capture your conversation with audio
The voice memo function on your phone or computer is a good choice when you’re in the middle of cooking or traveling and your relative surprises you by telling a story. You can quickly record them without missing a detail.

On iPhone, use the robust Voice Memo app. (It’s in your utilities folder, but for easier access, put it on your home screen.) On Android, use the built-in Sound Recorder app or download any of a variety of free or paid audio apps.
Shoot video of family stories
Using video adds even more color to a family story than just audio, but capturing it can be touchy. The last thing you want is for your Auntie to feel like the paparazzi are sticking cameras in her face, and you don’t want her to be focused on how she looks.
GenZ, Gen A, and younger millennials use their phones as if they are extensions of their fingers. Depending on your age and experience, you may be all-thumbs or quite adept at shooting video with your phone. The more easily you grab your phone and unobtrusively focus and hold it still, the more at ease Great-Grandma will be at telling her story of how she came to America.
If you can turn on your phone, set it up to stay steady, and give all of your attention to the narrative, everything will go more smoothly. Otherwise, develop a shorthand with your teen or tween, so while they play cinematographer, it lets you take the role of interviewer.
Set up a remote video call
The above options work great if you’re taking advantage of serendipity and spontaneously capturing a relative telling a story. But if you want to plan to capture memories, you’ll need to add some structure.
One good option is setting up Zoom, or any similar remote video service, and starting a conversation that way. There are a view key issues to consider:
- Ease of use — The basics of Zoom aren’t difficult; Paper Mommy is 88, and like most people, she took to using Zoom during the pandemic. But the email invitations, with the myriad links and phone numbers, can be overwhelming to users of all ages. When you set up a call, make sure that your interviewee(s) have as little confusion as possible; pare down the instructions to the absolute essentials or do it when someone in the family or a friend can help them set up. Nobody is at their storytelling best after thirty minutes of fighting their technology.
- Preparation vs. capturing lightning in a bottle — You know your family members. Some might freeze up if they’re asked questions; if their Nervous Nellies, send them at least a few of the prompting questions a day or two in advance. Other folks work best when they are spontaneous. You’ll need different methods for different family members.
- Recording — Pick a robust video platform option that allows you to record the call and access the file quickly and easily.
- Screen-sharing and other features — If you want to use photos to help prompt someone’s recall, make sure your video platform has a screen-sharing function, and set up the photos in a folder or slide-show, so you aren’t so distracted by the fiddly stuff that you break up the flow of your storyteller’s narrative.
You can work your way through the prompt questions I provided last week, but be sure you leave space for them to go off on tangents and surprise and delight you with unexpected tales!
Incorporate family photos into their stories
If you are handy with DIY, there are online companies where you can combine photos and text (like family stories) into a photo book (or a series of them). Popular sites include:
- Shutterfly — Browse from a collection of templates, select one, and upload your photos in JPEG format) into the pre-selected slots. Then add text, design elements, and other customizations. Shutterfly also has a free 24-hour designer service.
- Mixbook — Customize the design complexity and apply styles and themes.
- Google Photos — With prices starting at $14.99, you can customize hardcover or softcover book with custom captions, text, and collages on any page.
The above options help preserve visuals, but offer limited space for narratives.
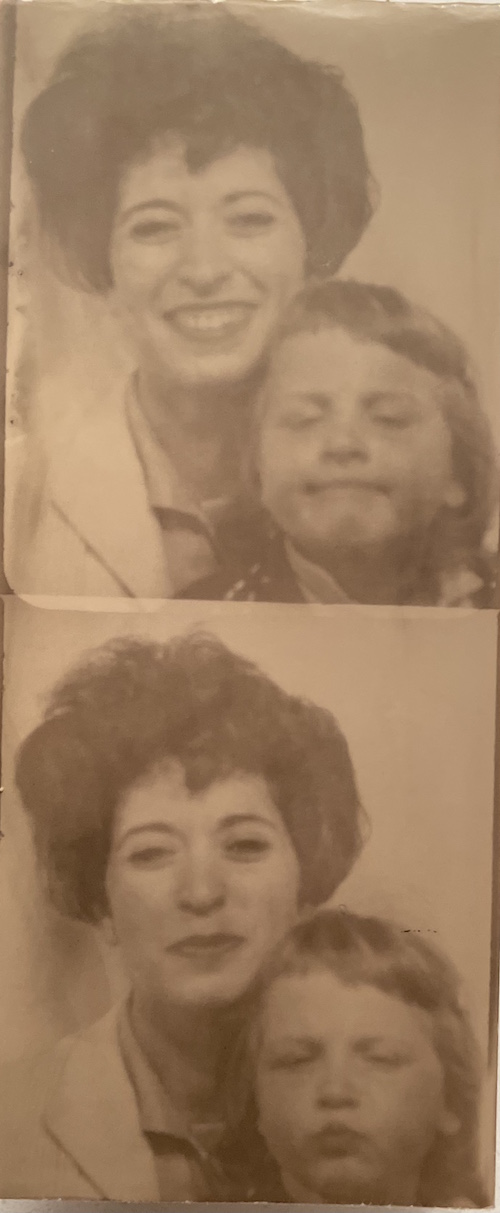

These snaps of Paper Mommy and my sister illustrates just one of a several family stories regarding my mother doing our hair. Here, Paper Mommy zealously, lopsidedly cutg my sister’s bangs. Luckily, there are no photos of the day I was sent out into the world with pink hair-setting tape still in my hair.
However, if you’d prefer a more white glove service rather than fighting with online settings, consider something like Jiffy Page‘s Pixorium. I’ve worked with clients to help them pare down their photos and then hand them off to Pixorium to scan and preserve digitally. They do a stellar job, but where they really shine is in helping develop custom story books.

Pixorium doesn’t just help preserve photos and make story books. Jiffy’s people are storytellers. Bring your photos, tell your story, even provide a manuscript of family history. Pixorium will listen, ask questions, and create a book that respects and reflects your family’s legacy. (Be sure to check out Pixorium’s YouTube page for great photo and legacy advice.)
Explore creative options for collecting family memories
The above options are more familiar, straightforward approaches to getting your family to tell stories and capture them, but if your family is up for some adventure, try something atypical.
This summer, I was intrigued by Perfect Pixel Moment‘s blog post on Medium, 12 New Ways to Preserve Family Memories, which included ideas like creating a family podcast series, developing a family blog, producing multi-generational family cooking videos, and more. Check it out.
What to do with what you collect
What you do with the notes, audios, and videos you capture is up to you. As with tangible organizing, you have to sort, merge, and edit your specific categories before organizing things into final form.
Whether you share raw footage or edit everything into a meaningful presentation, a documentary, or private YouTube channel is your choice. For now, focus on gathering and preserving the information while your storytellers are with you and up to the task of narrating their rich histories.
PLATFORMS FOR CAPTURING FAMILY MEMORIES IN BOOK FORM
There a huge number of services and apps designed to help you collect, organize, preserve, and share your family’s memories. The rest of this post explores just a few.
Storyworth
Storyworth is a subscription-based service. You select a weekly email prompt from the database of hundreds of “tell me about your life” questions. Your recipients respond with their own emails.
Unlike the broad, overarching prompts I suggested in last week’s post, Storyworth’s questions are more pointed and varied, including, “Can you sing your favorite lullaby?” and “What is one of your greatest fears?” (You can also edit the suggested questions or use your own.)
Stories are private by default and available to download by only authorized family members. At the end of the year, the responses to the prompts are bound into a book.

A standard package includes a year’s worth of weekly story prompts to help you interview one “storyteller,” online access for an unlimited number of family members (as authorized by you), and one 6″ x 9″ hardcover book with a black & white interior and a full color cover.
You can’t apply any of your own formatting, change fonts, etc., but the books can include photos. (The storyteller attaches photos to their email responses.) Once the responses are submitted, you and/or the storyteller can log in and edit responses and add captions to the photos, though some online reviews have mentioned the editing process can be finicky.
Extra books can be ordered, as follows:
- $39: Black and white interior, up to 480 pages
- $79: Color books, up to 300 pages
- $99: Color books above 300 pages, up to 480 pages
If you purchase multiple subscription packages, you can opt to blend multiple family members’ stories into one book.
A package is $99 for a year, with domestic shipping included.
Founded by Nick Baum to capture his father’s stories, Storyworth is independent and family-owned, and has been in business for over a decade.
Storyworth is best suited for a loved one who is comfortable with technology, in good enough health to read on-screen prompts and reply on their own, and eager enough to overcome procrastination or inertia and respond to a weekly email.
You know your relatives best. Will they feel like this is homework to slog through or an opportunity to shine?
Because stories are captured in print form (even with photos), they lack the vividness of platforms with audio and/or video. However, history tells us that print books will always be accessible, while digital A/V formats quickly become obsolete.
My Life In a Book
A similar biographical approach is offered by My Life in a Book, with questions selected from a database (though you can create your own questions to reflect the uniqueness of your relatives’ experiences).
Prompts come to your recipient via email, and replies are returned similarly, though there is a voice-to-text option, which allows someone to narrate stories directly into the online system.
Additionally, unlike the weekly flow of Storyworth, My Life in a Book allows you to customize the frequency of the arrival of the questions. Chatty Cathy can get them faster; Silent Sam can be asked less often.
This platform has a more structured biographical approach, with themes for the books:
- Preserving Memories fits the theme of tracking the lives of parents and grandparents
- Baby’s First Moments preserves important memories for new parents
- The Story of Us helps couples track their lives together
- I’m Writing a Book About You lets you create a book for and about a special loved one
My Life in a Book offers collaborative editing, so both the storyteller and any family members with access can help edit responses and even add photographs. You can also get real-time notifications to update you when your loved one has responded.
Users have input into the final book, including selecting from a variety of cover designs, choosing from a palette of color themes, and choosing different cover font text (but not interior fonts). Depending on the selected style, you may either select a pre-designed image or use a custom photo.
My Life in a Book is also $99, and shipping of books is free domestically and to Canada, UK, Australia, and New Zealand; there are shipping fees to other countries. Upgrades (at additional cost) include audiobook versions, additional print copies, and gift boxes for print books.
Remento
Remento is a worth considering if your loved one might feel more comfortable narrating a story rather than typing it.
There are still weekly prompts (which can include user-provided photo prompts), but the storyteller speaks the response into the system using a smartphone or computer; there are no logins or downloads, and reviewers report that it only requires a few clicks to get started.
Remento records and transcribes the recordings into stories printed as hardcover books.
Additionally, the books are printed with QR codes, which, when scanned, play the original recording used to write the chapters. Thus, future generations not only get the book, but get to hear the voice of the storyteller (at least as long as Remento is in business).
Remento uses artificial intelligence. Once the narration is recorded, you get to choose your preferred writing style (first-person, third-person, or transcript). From there, Remento’s Speech-to-Story™ AI technology turns your storyteller’s voice into a polished, edited written narrative. You can also customize the book’s title, color, and cover photo.
Remento is currently priced at $99, for which you get unlimited prompts and recordings, unlimited collaborators, and one premium, color-printed book. (If you subscribe to their mailing list at the bottom of the front page and are willing to get updates and notifications for sales and giveaways, you get $10 off.)
Remento is a little more focused on the journey (involving the whole family in encouraging responses to the prompts) than the destination (creating a book). All authorized family members can collaborate, watch the recordings as they’re submitted, send reactions to what’s been created (thereby providing the family storyteller with positive feedback), and select new prompts for future use.
As with the above options, your loved one will still need to keep up with prompts to get value, but the easy audio interface may make the experience more inviting than having to reply in writing.
Getting reactions on each uploaded story may be a positive experience (like getting a thumbs-up “like” on Facebook) or might be distracting and yield self-consciousness.
MULTIMEDIA PLATFORMS FOR PRESERVING FAMILY HISTORY
Books are fabulous, and your great-great-great-great grandchildren will probably be able to read text, as long as it’s not written in cursive. But if you want your family’s memories to come alive, and you want your own grandchildren to feel like they really knew your grandparents, there’s no substitute for audio and video.
StoryCorps
StoryCorps is a grand-daddy (or grand-mommy) of preserving family legacies, dating back to 2003, but it comes at it from a different perspective from most other platforms.
StoryCorps is a nonprofit project founded by a public radio producer, committed to the notion that we all have important stories to tell and that ALL of our stories matter. StoryCorps mission is to “help us believe in each other by illuminating the humanity and possibility in us all — one story at a time.”
I have a lump in my throat just reading that!
StoryCorps has a collection of more than 700,000 stories, the largest archive of its kind. Rather than creating a recorded family history for just generations of your people, you can create a story for future generations of people all over.
You have a few options for creating stories:
- Record with StoryCorps’ self-directed tools. If you can get in the same room with your loved one, use the StoryCorps App. Use my prompts from last week’s post, invent your own, or use StoryCorps’ prompts — then ask away. Alternatively, if your loved ones are elsewhere, whether across the city or across the world, you can record stories together via your web browsers using StoryCorps Connect. Either way, you can preserve your conversations using StoryCorps DIY resources.
- Alternatively, you and a loved one can record a conversation at one of the StoryCorps recording sites with the help of a facilitator. This adds a nice professional layer to the question-and-answer experience and may help your loved one feel more inspired. At the end of the session you get a recording of your interview and a copy is sent to the American Folklife Center at the Library of Congress. Talk about legacy!
- StoryCorps Mobile Tours — Each year for the last 15 years, StoryCorps has been going on a nationwide mobile tour. As I was writing last week’s post, I just happened to learn that they’re just up the road from me in Knoxville, TN, through the end of the month!
- StoryCorps Atlanta Booth — The StoryCorps facility at the Atlanta History Center has recorded and preserved thousands of conversations since 2013. If you’re in or near Atlanta, book an appointment to “interview” your loved one in person or even virtually, by phone. (They can feel like they’re on NPR, being interviewed by Terry Gross or Mary Louise Kelly!)
- Military Voices Initiative — This program provides a way for service members, veterans, and military families across America to honor and listen to their loved one’s stories. Book an appointment to preserve their memories (and your questions) in person or virtually at one of their Military Voices Initiative stops.
Some segments may even air on NPR, and I’ve seen beautiful StoryCorps personal histories set to animated video on StoryCorps’ TikTok channel. In fact, the following video prompted this part of the post series.
For more stories, see StoryCorps’s archive and YouTube page.
StoryCorps is free to all users.
Obviously, StoryCorps isn’t the right option for capturing an entire lifetime of memories, let alone the stories of all of your loved ones. However, the professionalism of the production experience may inspire your family members who may be dubious about having something to say, or who are shy about sharing their stories, to open up a bit. Consider StoryCorps as a way to delight in the storytelling experience and use it as an on-ramp for refreshing memories.
STORII
Storii recognizes that not everyone is going to be comfortable with typing their stories or even clicking around on an app or website. It’s designed for Great-Grandpa, who grunts at computers and cell phones whenever he sees them in public. (And for folks who, for whatever reason, have difficulty with technology.)
Storii uses actual phone calls to collect memories. Unless Great-Grandpa predates Alexander Graham Bell inventing the telephone in 1876, I think you’re safe.

Set up an account profile (in Storii’s iOS or Android app) for your loved ones to receive phone calls, whether on a cell phone or landline; alternatively, they can call in. (No smartphone or internet is required.)
Next, choose prompting questions from more than 1000 life story questions in their database (broken down into guiding categories like life, family, religion, career, or legacy), and/or craft some of your own.
Schedule up to three automated incoming calls per week at a time you know is good for your loved one, or arrange for them to call in to record their responses. Storii records and transcribes the calls, and adds them to your profile.
Record interactive responses. You and other family members can listen to the recordings and respond with audio, video, photo, and text responses.
Access the recordings as audiobooks or downloadable PDF books. Recordings can be shared with other family members by secure links or via emails.
If you think your storytellers won’t be at ease if they’re “surprised” by a question (even on a scheduled call), there are a few options.
They (or you) can log in to their Storii profile to see all upcoming questions (and remove, re-order, or add custom questions). If your loved ones don’t have (or don’t want to use) internet, and aren’t keen on getting you involved, they can call in to Storii at any time to hear their next upcoming question.
They can also just hang up after they hear the question on the scheduled call, and Storii will keep asking the same question until it’s either answered or skipped.
Storii’s pricing is $9.99/month or $99/year.
We have just scratched the surface of the DIY options and formal platforms for capturing, organizing, and preserving your family’s stories. But Paper Doll has one more trick up her sleeve. Next week, we’ll close out this series with AI-assisted platforms and apps for creating those family legacies. See you next time!
How to Collect, Organize, and Preserve Family Memories and History (Part 1) — The Questions

It’s hard to believe that we’re in the final stretch of the year; next month will be Thanksgiving, with the various winter holidays coming up right behind. It may be a joyous time spent with family or one marked by an empty seat at the table, a time of sharing new and old stories and, sometimes, grieving the questions un-asked and stories never told.
Over the next two posts, we’re going to look at ways of gathering and preserving your family stories so that future generations will have no regrets about what they’ve missed.
PAPER DOLL’S FAMILY HISTORY (AND FICTION)
Paper Doll is naturally curious. I have annoyed Paper Mommy (both as a child and as an adult) by insistently begging for tales. “Tell me a story about your grandparents that I haven’t already heard!” or “Tell me about when you were in school!” I urge my mother, to her frustration. She retorts, “I tell you things when I remember them. I can’t call up stories at the drop of a hat!”
As someone who is practically built out of words and memories, I can’t fathom it. Ask me about my first day of kindergarten, or my first date (an extremely embarrassing skating story everyone somehow remembers clearly) or the day I bought my car, and I can recite it as if it happened thirty minutes ago.
My family finds this annoying.
I find the lack of stories annoying. I want a complete biography, with footnotes, of my mother’s life — every conversation and experience I missed from the day she was born until I was a toddler, I want filled in. And the ones I know by heart, I still want to hear her tell them over and over again, complete with accents and narrative flourishes.
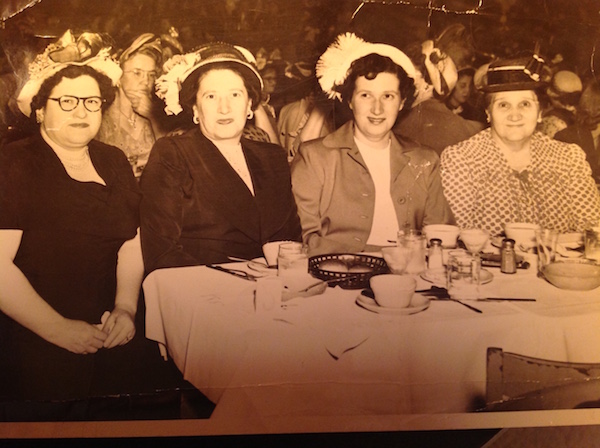
My favorites? The time in her nursery school education class where the miniature turtle went missing after the toddlers left, but (after a length search) was found in the back of a teeny toy dump truck. The time when my great-grandmother, who ran terrified of a dog chasing her from the streetcar and hid on the floor of the closet during thunderstorms, nonetheless ascended a ladder and climbed in a window when she was locked out of the house. (That’s my mother’s Bubbe on the far right, below.)

I know how my mother’s father came to America. He, his father, and his brother set out from home in Poland so his brother could take a boat to America, but (as you likely learned in Social Studies), people with diseases of the eye could not be admitted. (It’s an imprecise analogy, but imagine your nine-year-old’s pinkeye caused your family to be turned away at Disney World!) My great-uncle’s suitcase was thrust into my grandfather’s hands, and the teenager set off for America.
I’ve heard a few stories about my Poppy, some surely apocryphal. (Only many decades later did we start to doubt the tale of his job unloading cargo on the docks: a burlap bag of chocolate burs open, upon which he and his fellow worker filled their pockets with chocolate and ran away. Um, did chocolate ever come wrapped in nothing but burlap?)
Other stories were also questionable, such as when he told of a man running a food cart being asked for a hot dog. The cart only served fish, so the cart owner gave the man a fish sandwich, and the man was heard saying it was the best-tasting hot dog he’d ever had! (Years later, my grandmother, feeding my toddler uncle, urged him to eat the yummy hot dog he’d been requesting. It was a soft-boiled egg. Perhaps my Poppy’s story was the catalyst?)
Still, there are verifiable stories. My grandfather bought part ownership of a decommissioned battleship as scrap metal, and later owned an apartment complex he named after my sister. A friend researching genealogy found a Depression-era news article about him being robbed of of hundreds of dollars cash (because he didn’t believe in banks) but was not destitute because he’d also hidden money in his socks.
And once, my mother exited a downtown summer camp reunion luncheon to find her father — a Jewish man from Poland — at the head of Buffalo’s St. Patrick’s Day parade!
And yet, we know nothing of his life before he came to America except his mother was tall and that his father was, circa 1910, the captain of the town’s fire brigade. When my maternal grandparents were visiting in the mid-1970s, my grandfather slipped on the Buffalo ice and went to the hospital. Fed up with the pesky questions demanded by the hospital, my grandmother snapped when the nurse wanted my grandfather’s mother’s name, and made up a random name that sounded shtetl-appropriate.

Paper Doll with Poppy, circa 1968 or 1969 (The booklet we’re “reading” says it “will tell you how you can become a Computer Programmer.”)
As I described in The Great Mesozoic Law Office Purge of 2015: A Professional Organizer’s Family Tale, it was only when I closed down my father’s law office that I connected with his cousin and learned that my paternal grandfather, whom I always imagined to have grown up in vague immigrant-era poverty, was decidedly more Upstairs than Downstairs.
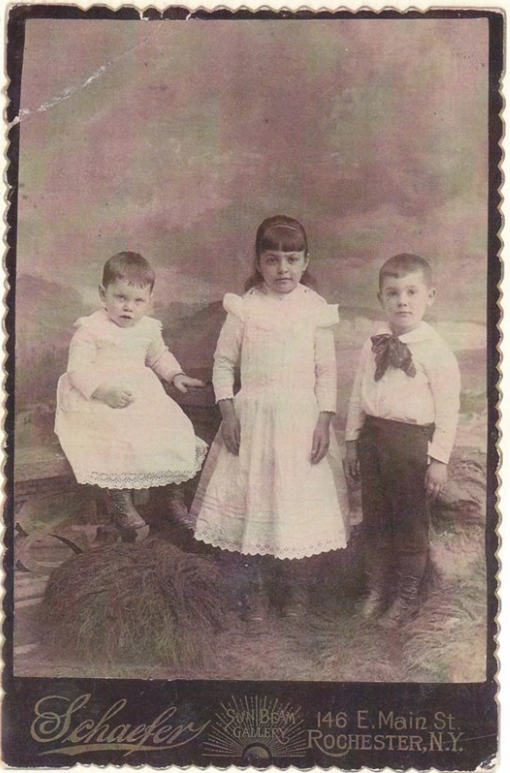

Indeed, until recently I knew nothing of my father’s father’s family, and have been fascinated by what my genealogist friend’s have found. I didn’t even know my great-grandfather’s name before reading this obituary, let alone that he owned a hardware and tinsmithing store. (When was the last time you heard about “tinsmithing?”)

I only knew of two of my grandfather’s sisters; two others plus a brother were surprises to me. Nor had I learned that my grandfather’s brother became a Broadway performer and impresario! Why was I never told these stories? My father was more interested in his future than his family’s past, I suppose.
Speaking of my father, he was a clotheshorse and chronically disorganized. So, I was amused to find this post, referencing my Great Uncle Mike “Harry” Bestry:
Damon Runyon wrote in Short Takes, for example, that Harry Bestry owns or owned “3,000 Charvet neckties, which is more than Charvet has now, 75 suits of clothes by an expensive tailor, 75 pairs of shoes, each pair made to order and nicely treed, and hats and shirts and overcoats and sweaters in similar profusion.” He added that a friend of Bestry once reported one could barely get into the man’s apartment “because of the amount of wearing apparel stashed away on the premises.”
There’s something odd about knowing that the person who created Guys & Dolls wrote about my relative. Odder still that this could absolutely have been a description of my own father.
When I was home in June, helping downsize and declutter the family basement, I found a scrapbook my father’s first wife made of their trip to New England in 1951 and a few after that. His bride’s careful penmanship next to each piece of memorabilia detailed not only their trip, but the era. On the same page, she extolled the virtues of a restaurant meal but also noted the antisemitism of the hotelier announcing that the hotel — at which my father and she (both Jewish) had been welcomed — was restricted. No Jews allowed. (They departed before nightfall.)
[If you’re unfamiliar with this era in American history, you might want to see the Gregory Peck film based on the Laura Z. Hobson novel, Gentleman’s Agreement, in which Peck plays a journalist who goes undercover as a Jewish man to explore post-War antisemitism.]
As I reviewed the scrapbook, I absorbed the details of each crumbling page which had been lovingly assembled over seventy years ago by a woman who died perhaps sixty years ago. I was fascinated by the notations of someone to whom I had only a tangential relationship, narrating weeks in the life of someone with whom I shared half my DNA.
Of course, family history comes with world history. I was fascinated by the prices on the menus.

At Keeler’s State Street in Albany (established 1864), a whole baby pheasant with sides of lima beans and wild rice could be had for $3.50, with desserts from 30 to 60 cents. (Eat up quickly! Parking was twenty-five cents an hour!)
Meanwhile, New Orleans’ Restaurant Antoine (founded 1840, and which still exists) cost them a prettier penny. It was a multi-page menu, but my focus was on the eye-popping price of $7 for chateaubriande! Splurge further: $1.25 for a Crêpe Suzette for dessert.

WHY CAPTURE YOUR FAMILY HISTORY?
This is all to say that if you aren’t inclined to ask, and if your relatives aren’t inclined to tell, it can be difficult to create any sense of family legacy, either for yourself for for generations that come after.
In her excellent book, What’s a Photo Without the Story?: How to Create Your Family Legacy, my friend and colleague Hazel Thornton details why you might want to gather your stories and those of your family and your ancestors. At the start of the book, she explains that doing so will:
- Give depth and meaning to your photos.
- Make history come alive!
- Preserve family legends (rumored or proven).
- Give children a sense of belonging and help them feel more secure.
- Make us feel connected to our families , and to the world around us.
- Help us better understand our families, and ourselves.














Follow Me